Is there a treatment for MPS I?
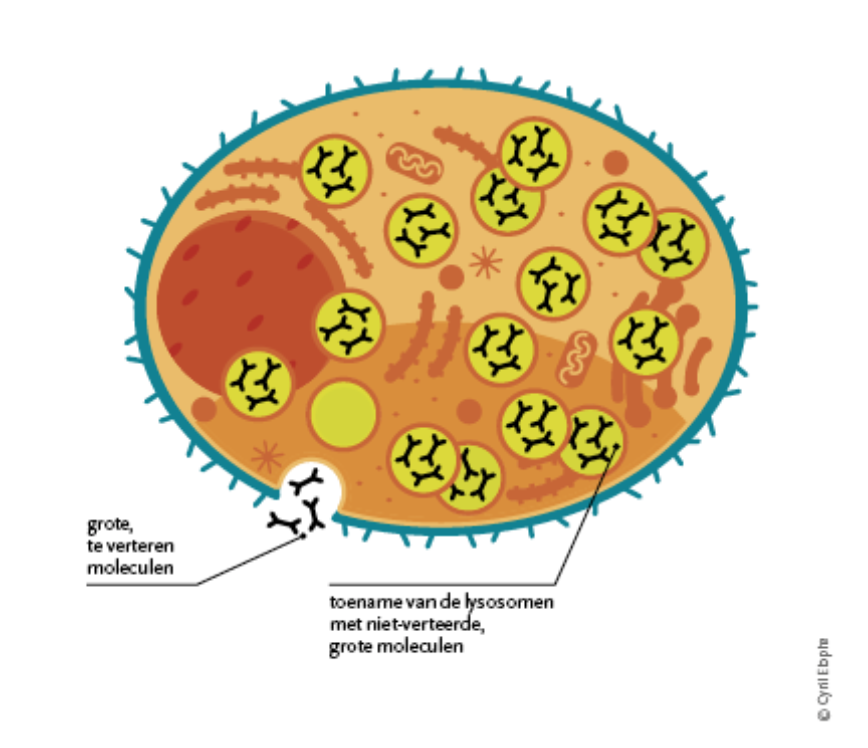
Individuals with lysosomal storage diseases cannot produce sufficient specific enzymes for the body to work properly. These enzymes, which cause the breakdown of a large number of different types of substances, are not present at all or only in very small quantities.
The result is an accumulation of material that disrupts the normal functioning of the cells, affecting organs, which can lead to life-threatening problems.
The diagram below explains the processes behind a lysosomal storage disorder.
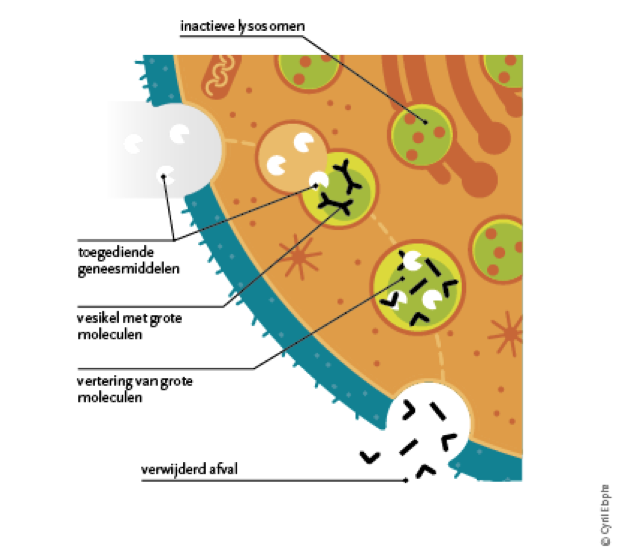
With MPS I, the body is unable to produce the enzyme alpha-L-iduronidase that is needed to excrete certain waste products. Researchers have developed a treatment to replace that enzyme in the body: enzyme replacement therapy.
Since 2003, enzyme replacement therapy has been available in Belgium for the treatment of MPS type I.
Enzyme replacement therapy
In this therapy, the missing lysosomal enzyme is replaced by infusions with an enzyme that is very similar to the missing human enzyme.The treatment consists of regular infusions of the missing enzyme to ensure that the metabolism (metabolism) can return to normal and stops the accumulation of the waste.
Enzyme replacement therapy is given once a week, administration of the infusion takes a few hours (depending on the weight of the patient).
There is increasing evidence that the earlier the treatment starts, the better the results will be. The course of the disease can be delayed or changed and late complications can be avoided, which can significantly improve the quality of life of many patients. However, it is important to note that enzyme replacement therapy has no effect on nerve damage in patients with the most severe form of MPS I. The therapy only affects the non-neuropathic symptoms. This is because the enzyme cannot pass through the blood-brain barrier.
Supportive care and treatment of complications.
This type of treatment helps alleviate the symptoms, but does not address the underlying cause of MPS I. Some examples of supportive care:
- Extra oxygen in case of breathing difficulties
- CPAP machines (continuous positive airway pressure - continuous positive air pressure) in case of interrupted breathing during sleep (sleep apnea)
- Surgical procedure (tracheostomy) in case of breathing difficulties
- Physiotherapy in case of stiff joints
- Heart valve replacement in case of heart problems
- Bone marrow transplantation and umbilical cord blood transplantation.
For a number of eligible patients, a bone marrow or umbilical cord blood transplant may be a suitable treatment. This procedure is usually applied to younger patients who have the severe form of the disease. You evaluate the risks and benefits of each of these treatments with your doctor.